Interferogram Simulator
This code provides a dataset simulation method that can provide training samples with strong generalization ability for model training. Deep learning, as a data-driven method, requires a large number of training samples to train network models. However, it is difficult or even impossible to obtain ground truth corresponding to InSAR data because it is difficult to collect high-resolution ground deformation information, which limits the application of deep learning in the field of InSAR. In this paper, we study the phase characteristics of a large number of real interferograms, analyze the statistical models of InSAR data and noise sources, and propose a strategy to construct training samples by simulating the phase components of terrain, buildings, deformation, atmosphere, water surface and noise separately, which is applicable to training networks for different tasks such as interferogram denoising, deformation detection and phase unwrapping. Experimental results show that this dataset simulation method can effectively train deep network models with good generalization ability on real data.
Access the source codeTutorial
The code is based on MATLAB, make sure MATLAB is installed.
Clone the repo:
1
2git clone https://github.com/Wu-Patrick/InterferogramSimulator.git
cd InterferogramSimulatorRun with MATLAB:
1
main.m
You can easily modify the parameters to obtain different data sets.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37%%% Control parameters %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
params.savePath = 'data/test';
% Data saving path
params.totalNum = 50; % Total number of samples
params.sampleSize = 256; % Size of generated sample
params.multilook = [1,4]; % multilook [Azimuth, Range]
params.demFolder = 'DEM/unzip';
% Folder path containing multiple DEM (*.tif format)
% You can download DEM files from: https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/srtmdata/
%%% output %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
params.savePNGFlag = 1; % Save the *.png image corresponding to the data
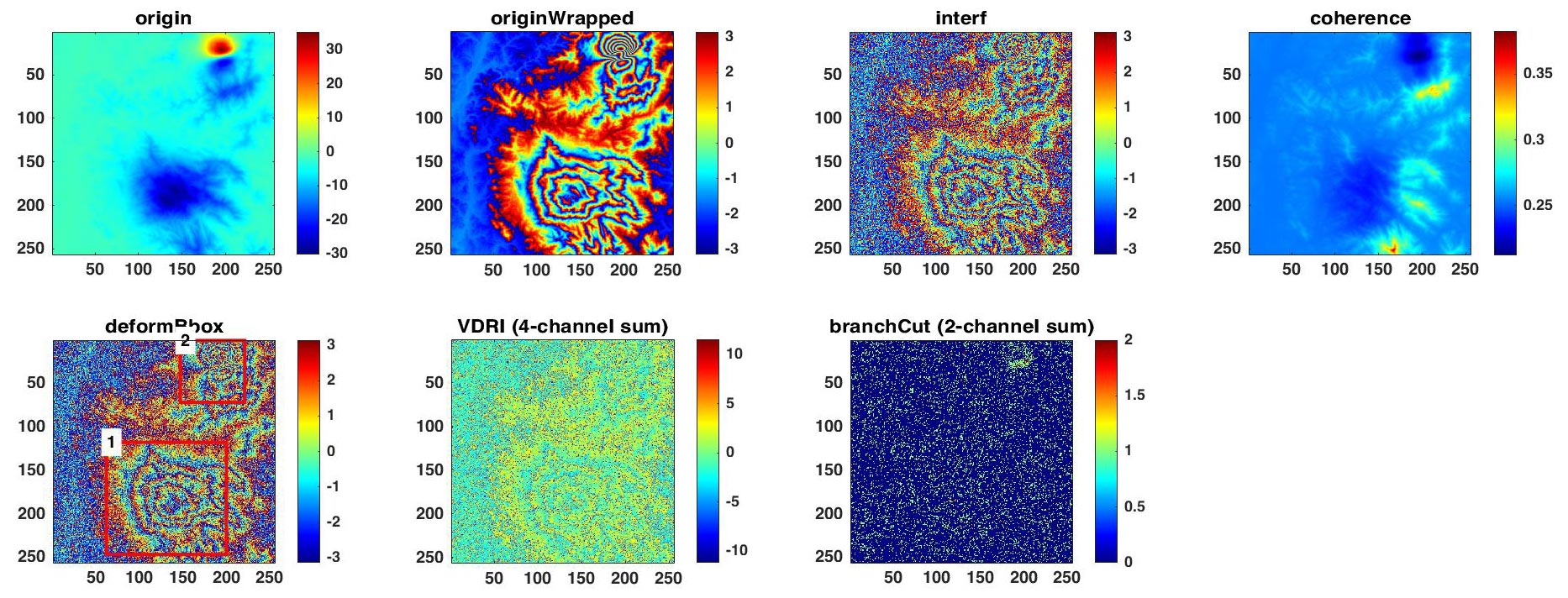
params.out.origin = 1; % Original phase
params.out.originWrapped = 1; % Wrapped version of the original phase, i.e., noise-free interferogram
params.out.interf = 1; % Simulated interferogram
params.out.coherence = 1; % Estimated coherence
params.out.deformBbox = 1; % Location and category of deformation area
params.out.VDRI = 1; % Horizontal phase gradient + residual map
% + vertical phase gradient + interferogram (4 channels)
params.out.branchCut = 1; % Horizontal branch-cut and vertical branch-cut (2 channels)
% You can customize other types of output and implement them in "generateOne.m".
%%% Add phase components with a certain probability (0-1) %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
params.probSlop = 0.1; % Slope phase
params.probBuilding = 0.2; % Building phase
params.probTurbulence = 0.8; % Atmospheric turbulence phase, i.e., fractal Perlin noises
params.probDeform = 0.2; % Distorted two-dimensional Gaussian surface
params.probEarthquake = 0.2; % Deformation caused by earthquakes
params.probWater = 0.5; % Completely decorrelated area (water area)
params.noiseType = 0; % 0 : Deformation-related noise
% 1 : Noise with random signal-to-noise ratio, not recommended
params.noiseSNRRange = [0.2,5]; % Need to specify when noiseType=1
% Other parameters can be modified in the source code.
%%% Parallel %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
params.Parallel = 1;
Examples
Citation
If you use this code, please cite the following:
1 | @ARTICLE{9583246, |





